|
15- Mechanism of Pd(II) and Hg(II) co-catalysis
in N-bromoacetamide oxidation of D-galactose and L-sorbose in
perchloric acid : A Kinetic Study
Ashok Kumar Singh*, Vinod Kumar Singh, Shahla Rahmani, Jaya
Srivastava and Bharat Singh Department of Chemistry, University of
Allahabad, Allahabad-211002, INDIA, ashokeks@rediffmail.com
(Received 15 December 2005; accepted 27 February 2006)
Abstract:
The kinetics of oxidation of D-galactose (Gal) and L-sorbose (Sor) by
N-bromoacetamide (NBA) in the presence of Pd(II) as catalyst and
Hg(II) as co-catalyst are presented. The reactions follow identical
kinetics, being first order in both substrates and Pd(II). The first
order kinetics with respect to NBA at low concentrations tends to
zero-order in its higher concentration range. Positive effect of
[Hg(II)] and decreasing effect of [H+], [Cl-]
and [NHA] on the rate of oxidation of Gal and Sor were observed. A
zero effect of variation of ionic strength of the medium on the rate
of oxidation was observed. Utilizing the values of observed rate
constants at four different temperatures, the activation parameters
have been calculated for each reducing sugars. D-lyxonic acid and
L-threonic acid were identified as the main reaction products in the
oxidation of D-galactose and L-sorbose, respectively. The results are
in accord with a mechanism in
which the complex,
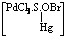 in the
rate determining step, decomposes into an intermediate which finally
changes
into products through a series of fast steps with regeneration of
effective species of the catalyst. in the
rate determining step, decomposes into an intermediate which finally
changes
into products through a series of fast steps with regeneration of
effective species of the catalyst.
Key words: Mechanism, Pd(II) and Hg(II) co-catalysis, Acidic
medium, Oxidation, Reducing sugars, N-bromoacetamide.
<<< |

